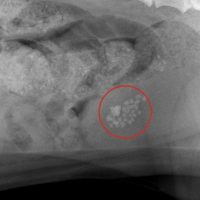
My cat suddenly began going to the litter box very frequently. A sample of urine revealed a bladder infection. How did this happen?
While urinary tract disorders are fairly common in cats, urinary tract infections (UTIs) are fairly uncommon. Cats with UTIs try to urinate very frequently, they may pass only small amounts of urine, they may strain to urinate, they may cry out or whine when urinating, and there may be blood visible in their urine. Urinating outside of the litter box is also a red flag that something is wrong in the bladder. Finally, frequent licking around the rear end may signal that a UTI is present.
Generally, a UTI occurs when bacteria travel up the urethra and into the bladder. Urine in the bladder is supposed to be sterile, but once bacteria find their way to the bladder, the bacteria can grow and reproduce, causing the UTI. Some cats will develop bladder stones, with or without a UTI, and this opens the door for additional health issues.
What does a urinalysis look at?
If your cat presents to your veterinarian with urinary signs, your veterinarian will first perform a urinalysis. The urinalysis can reveal so much important information about the urine when a UTI is suspected. Your veterinarian will look for the following:
- urine-specific gravity (how well the cat is concentrating their urine)
- pH (certain pH levels can indicate infection or other problems)
- ketones (sometimes seen in cases of diabetes or body-wasting)
- glucose (sugar in the urine, usually a sign of diabetes)
- bilirubin (a breakdown product of blood)
- blood
- protein
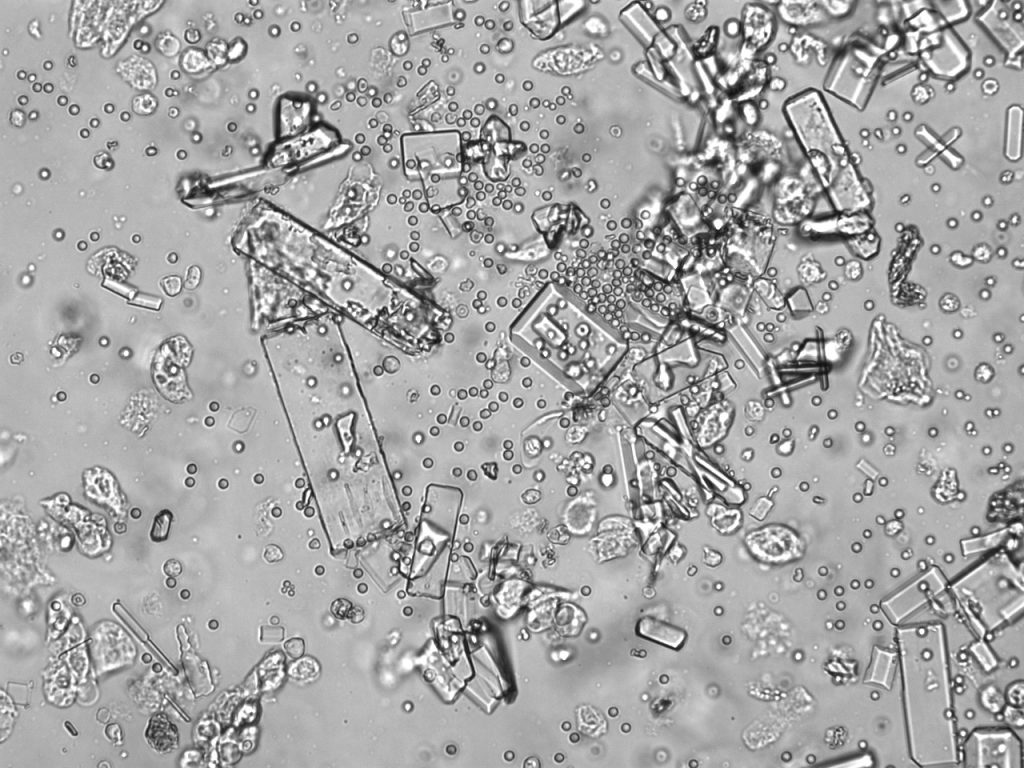

Once these levels are measured, the urine specimen is placed into a centrifuge and spun down to allow cells and other debris to accumulate at the bottom of the sample tube. That debris can then be evaluated, revealing the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, bacteria, and crystals.
My veterinarian sent a sample of urine to a laboratory for what she called a culture and sensitivity test. What is this?
All urinary tract infections are NOT created equal! Even though the most common organism to cause UTIs in cats is Escherichia coli (the bacteria found in feces), there are several other organisms that may be involved. The only way to identify which specific bacteria is causing the UTI, is to grow it in a laboratory. At the same time, the laboratory can also test which antibiotic is best suited to treat the infection.
Often, a veterinarian will prescribe an antibiotic that is among the most commonly used for treating UTIs in order to try to provide immediate relief to the cat. They may also prescribe pain medications (UTIs can be uncomfortable), and they may recommend a diet change.
Once the culture and sensitivity results are received, an appropriate antibiotic will be prescribed. After the course of antibiotics is given, it is important to recheck the urinalysis to confirm that the infection is resolved. If it is not, then it will be important to look for other issues that may contribute to a persistent UTI.
Are some cats predisposed to UTIs?
Older female cats, and cats with diabetes mellitus (sugar diabetes), develop UTIs more commonly than the general population. Cats who have bladder stones are prone to recurrent UTIs, pointing out the importance of getting a complete diagnosis whenever there are signs of disease in the urinary tract. Bladder stones must be removed or dissolved in order to restore bladder health.
What can I do to prevent a UTI from occurring in the future?
Your veterinarian will let you know if there is anything that can be done to prevent your cat’s UTI from coming back. There is evidence that specific diets can support lower urinary tract health. It is best to discuss UTI prevention and bladder health with your veterinarian in order to put into action an effective plan.
© Copyright 2020 LifeLearn Inc. Used and/or modified with permission under license.